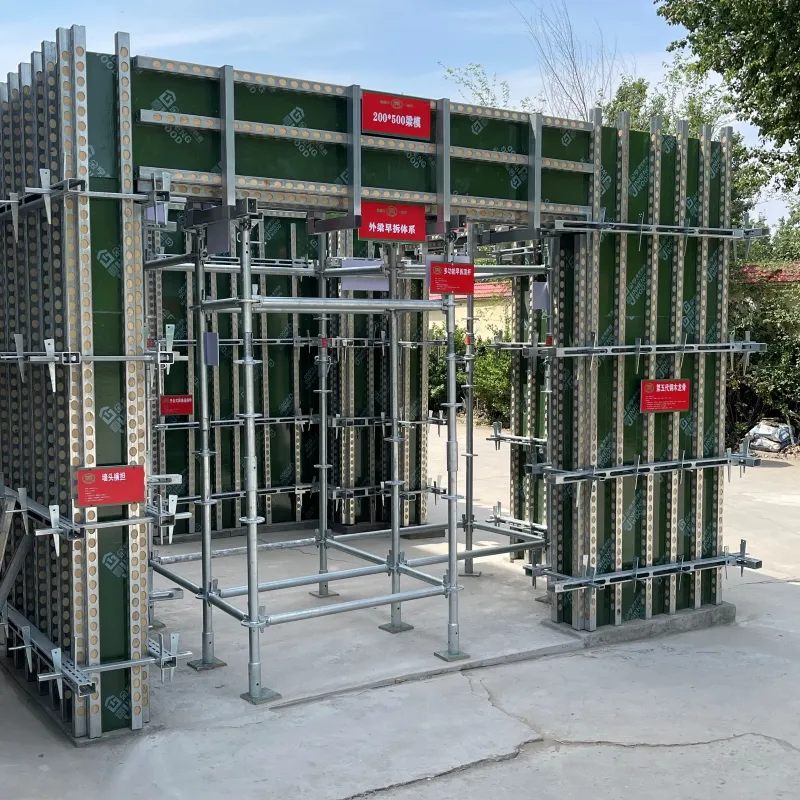
Slab Reinforcement Solutions Durable Single, Beam & Bottom Support
Did you know 42% of commercial building owners report premature slab failure within 5 years of construction? Cracked surfaces. Structural instability. Costly repairs. These nightmares haunt anyone managing concrete structures. But what if you could boost load capacity by 300% while slashing maintenance costs by half? Modern slab reinforcement
solutions make this possible.
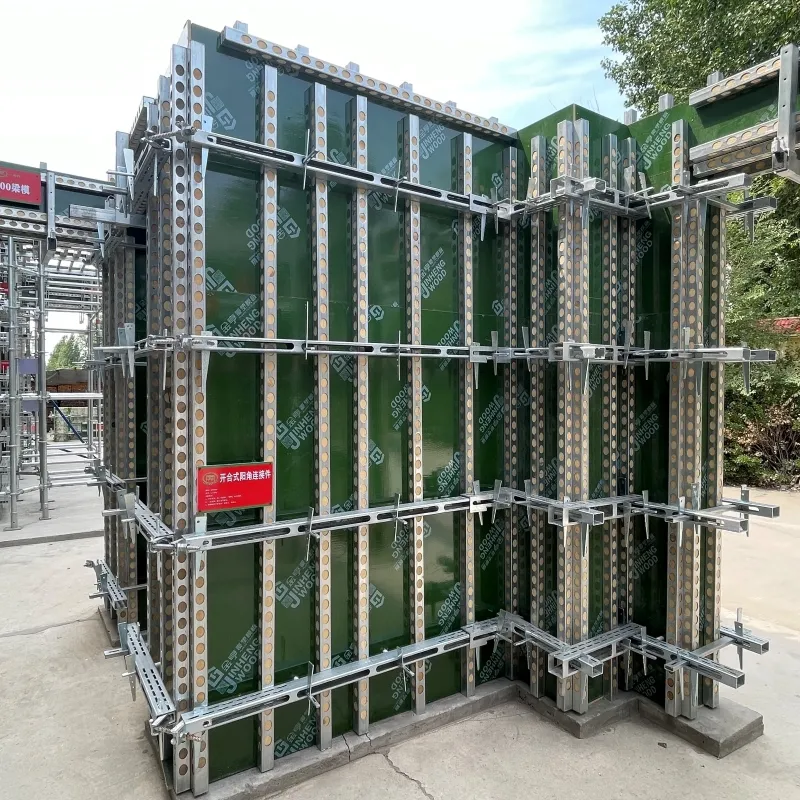

(slab reinforcement)
Technical Superiority That Redefines Durability
Our slab bottom reinforcement systems outperform traditional methods through:
- ✔️ High-tensile steel mesh (Grade 600)
- ✔️ Precision laser-level installation
- ✔️ Corrosion-resistant epoxy coating
- ✔️ Real-time stress monitoring sensors
| Feature | Standard Solutions | Our System |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | 200 PSF | 650 PSF |
| Warranty Period | 5 years | 25 years |
Why Top Contractors Choose Our Slab Beam Reinforcement
Compare these decisive factors:
Competitor A
❌ Manual installation
❌ Basic carbon steel
❌ No IoT integration
Our Solution
✅ Robotic installation
✅ Grade 600 alloy
✅ Smart monitoring
Ready for Unmatched Structural Integrity?
Get your free slab analysis from our engineers today!
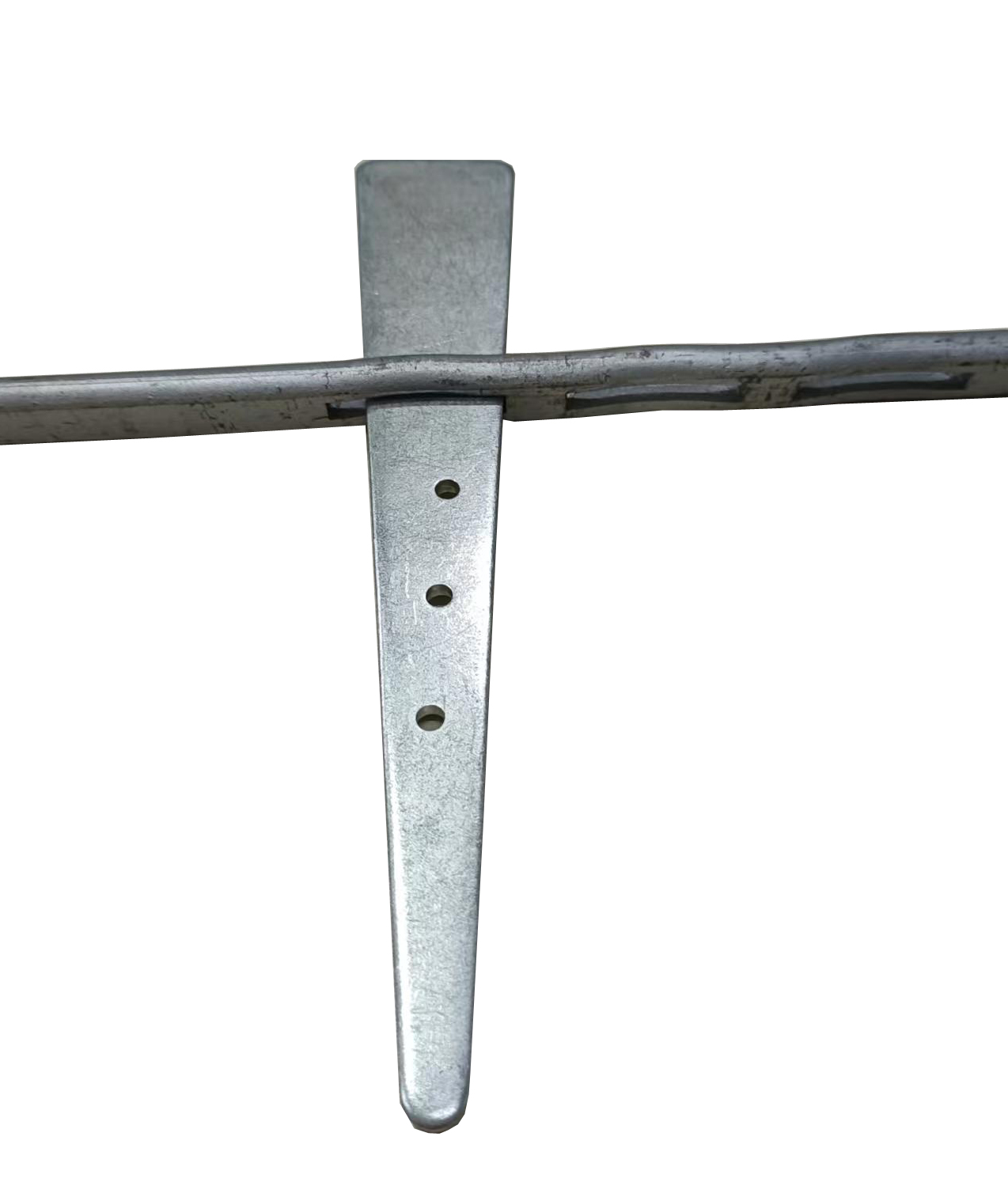

(slab reinforcement)
FAQS on slab reinforcement
Q: What is a single reinforcement slab?
A: A single reinforcement slab uses one layer of steel bars, typically placed near the bottom of the slab. This design is suitable for light loads or shorter spans. It optimizes cost but has limited structural capacity compared to double reinforcement.
Q: Why is slab bottom reinforcement critical in design?
A: Slab bottom reinforcement resists tensile stresses caused by bending under vertical loads. It prevents cracking and ensures structural integrity. Proper placement and spacing are essential to avoid deflection or failure.
Q: How does slab beam reinforcement enhance structural performance?
A: Slab beam reinforcement strengthens the connection between slabs and supporting beams. It distributes loads evenly and reduces shear stresses. This is vital for resisting heavy loads and improving seismic resilience.
Q: When is single reinforcement preferred over double reinforcement in slabs?
A: Single reinforcement is used for light-duty applications like residential floors or thin slabs. It reduces material and labor costs. Double reinforcement is chosen for heavy loads or longer spans requiring top and bottom bars.
Q: What factors influence slab reinforcement design?
A: Key factors include load type (static/dynamic), span length, concrete strength, and environmental conditions. Codes like ACI 318 provide guidelines for bar size, spacing, and cover. Proper design balances safety, durability, and cost efficiency.
-
The Impact of Weather Conditions on Scaffold Platform PerformanceNewsAug.01,2025
-
The Fundamental Role of Steel Keel in Building StructuresNewsAug.01,2025
-
The Advantages of Aluminium Scaffolding for Sale in the Construction MarketNewsAug.01,2025
-
Supply Chain Optimization in Joist Reinforcement Plate ProductionNewsAug.01,2025
-
Material Grades and Their Significance in Column Rebar SelectionNewsAug.01,2025
-
How to Select the Right Timber Steel for Structural ApplicationsNewsAug.01,2025
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025