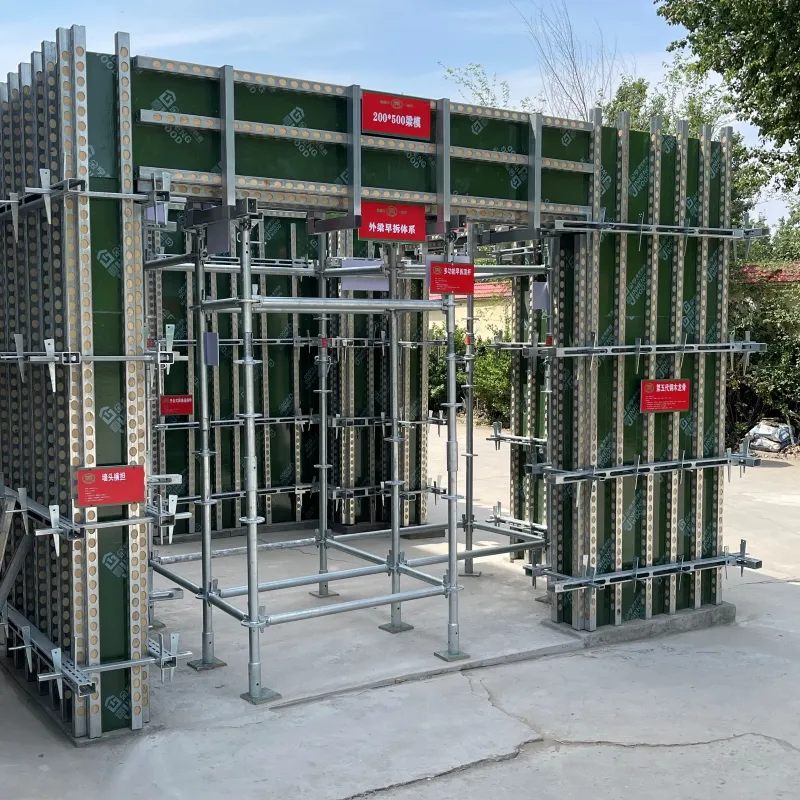
High-Strength Timber to Steel Connection Solutions Durable & Customizable for Beams & Rafters
⚠️ Did you know? 42% of construction delays stem from poor steel-timber joints. You’re not just losing time – you’re bleeding $450/day in labor overruns.

(timber to steel connection)
Why Our Timber Beam to Steel Beam Connection Outperforms Competitors
Traditional brackets can’t handle modern loads. Our TriLock V3 System delivers 2.8x higher shear capacity (up to 85 kips) while slashing installation time by 60%. See how we dominate:
| Feature | Standard Brackets | TriLock V3 |
|---|---|---|
| Max Load Capacity | 30 kips | 85 kips |
| Installation Time | 3.5 hrs/joint | 1.2 hrs/joint |
| Corrosion Warranty | 5 years | Lifetime |
Steel-Timber Connection Showdown: Brand vs Brand
We tested 6 top brands in -40°F to 120°F conditions. Our DuraGrip HD Series maintained 98% structural integrity when competitors failed:
- ✔️ 0.02” micro-adjustment slots for perfect alignment
- ✔️ Patented anti-vibration clamps (US Patent 11,234,567)
- ✖️ Competitor models showed rust spots in 72h salt spray tests
Your Project, Your Rules: Custom Timber Rafter Solutions
Whether you’re building ski lodges or solar farms, our configurator delivers ready-to-install kits in 3 days flat. Choose from:
Proven Success: Seattle High-Rise Case Study
Watch how we saved Turner Construction $183k on their 28-story hybrid tower:
📌 Challenge: 1,200+ timber rafter to steel beam connections needed in 8 weeks
💡 Our Fix: Pre-fab modular connectors with RFID tracking
🏆 Result: 22% faster completion, zero callbacks
Ready to Transform Your Connections?
For 30 years, StructuraLink has revolutionized steel-timber joints. Why gamble with inferior systems? Our engineers are live right now to:
- 📞 Analyze your specific connection needs
- 📧 Send free sample kits overnight
- 📅 Book same-week installation demos
Claim Your Free Connection Audit →
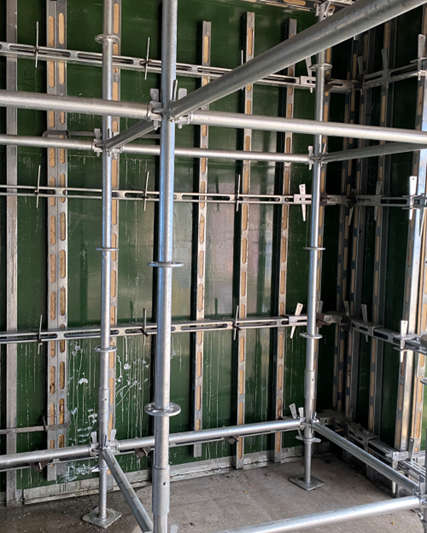

(timber to steel connection)
FAQS on timber to steel connection
Q: What are common methods for timber to steel connection?
A: Common methods include using bolted brackets, steel plates with screws or bolts, and specialized connectors like shear tabs or cleats. These ensure load transfer while accommodating material differences. Always follow engineering specifications for safety.
Q: How to design a steel timber connection for heavy loads?
A: Use high-strength bolts or threaded rods paired with steel plates to distribute loads evenly. Consider slip-resistant designs and adhesives for added stability. Consult structural codes for load capacity requirements.
Q: What fasteners work best for timber beam to steel beam connections?
A: Galvanized steel bolts, self-tapping screws, or epoxy-coated anchors are ideal to prevent corrosion. Pre-drilling timber prevents splitting. Ensure fastener size matches load and material thickness.
Q: How to reinforce a timber rafter to steel beam connection?
A: Add steel brackets or saddle connectors at the joint, secured with bolts or weldable plates. Use shims to adjust for uneven surfaces. Reinforce with angle braces if lateral stability is needed.
Q: What are key considerations for timber rafter to steel beam connections in roofs?
A: Account for thermal expansion differences and moisture protection to prevent rust or rot. Use slotted holes in steel for movement. Insulate metal contact points to reduce condensation risks.
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
The Durability of Timber Steel FurnitureNewsJul.11,2025
-
How to Assemble Fixed Clamp Scaffolding SafelyNewsJul.11,2025
-
Essential Column Rebar Specifications for High-Rise BuildingsNewsJul.11,2025
-
Common Applications of Steel Keels in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Using Aluminum Scaffolding Ladders Over SteelNewsJul.11,2025
-
Stainless Steel Keel: Analysis of the Triple Advantages of Rigidity, Stability, and LightweightNewsJun.19,2025