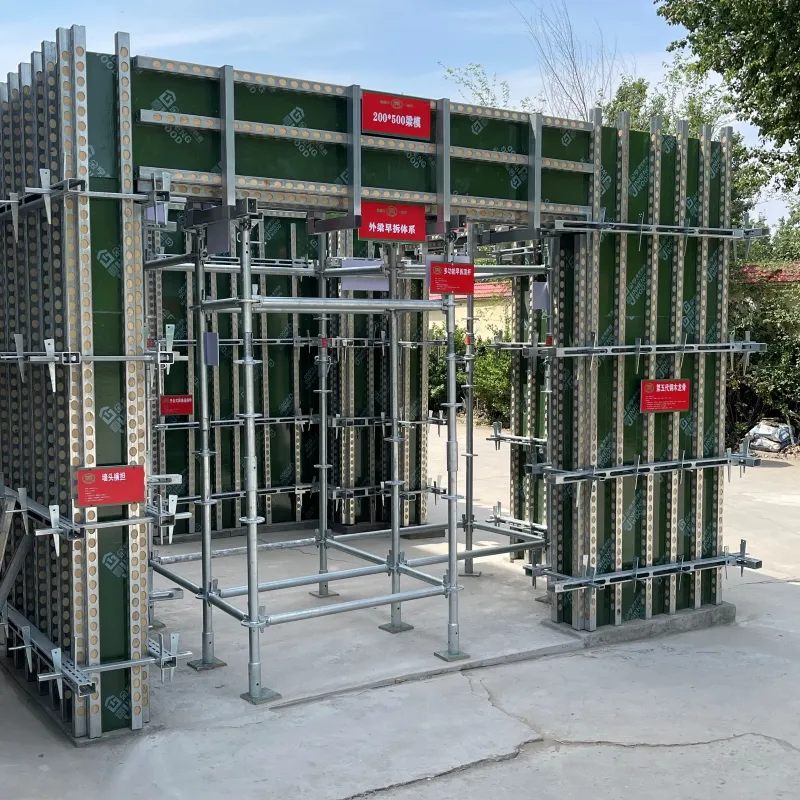
2nd Floor Concrete Slab Solutions Durable & Lightweight Designs
- Understanding the Importance of 2nd Floor Slab Construction
- Technical Advantages of Modern Concrete Slabs
- Comparing Leading Slab Manufacturers
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Structural Needs
- Case Studies: Successful 2nd Floor Slab Installations
- Cost Efficiency and Long-Term Durability
- Why Choose Specialized Slabs for 2nd Floor Projects

(slab for 2nd floor)
Understanding the Importance of 2nd Floor Slab Construction
Constructing a robust slab for 2nd floor
requires precision and expertise. These slabs serve as the foundation for upper-level spaces, balancing load distribution while minimizing structural stress. According to industry data, improper slab design accounts for 22% of residential construction failures. Modern slabs integrate reinforced steel mesh and high-strength concrete (up to 40 MPa), ensuring resistance to cracking and deflection under dynamic loads.
Technical Advantages of Modern Concrete Slabs
Advanced 2nd floor concrete slab systems leverage lightweight aggregates and post-tensioning techniques. These innovations reduce slab thickness by 15–20% while maintaining compressive strength. For instance, a 150mm slab with polypropylene fibers can span up to 6 meters without intermediate supports. Thermal insulation properties also improve energy efficiency, reducing HVAC costs by 12–18% in multi-story buildings.
Comparing Leading Slab Manufacturers
| Brand | Thickness (mm) | Weight (kg/m²) | Installation Time | Price per m² ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlabMaster Pro | 160 | 320 | 3 days | 85 |
| ConcreteTech Ultra | 140 | 290 | 2.5 days | 92 |
| StructFloor Plus | 150 | 310 | 3 days | 88 |
Custom Solutions for Diverse Structural Needs
Tailored slab 2nd floor designs address unique architectural challenges. Options include:
- Adjustable thickness profiles for uneven load zones
- Hybrid material blends (e.g., fly ash or slag cement)
- Embedded utilities routing for electrical/plumbing systems
Precast modular slabs now achieve 98% dimensional accuracy, slashing on-site adjustments by 40%.
Case Studies: Successful 2nd Floor Slab Installations
A recent commercial project in Chicago utilized 180mm post-tensioned slabs to accommodate a 500 kg/m² live load. The installation, completed in 14 days, reduced labor costs by $18,000 compared to traditional methods. Residential retrofits in seismic zones have also seen 30% faster completion times using fiber-reinforced slabs.
Cost Efficiency and Long-Term Durability
Investing in quality slab for 2nd floor systems yields 20-year ROI through reduced maintenance. Accelerated curing techniques cut project timelines by 25%, while epoxy-coated rebar extends corrosion resistance to 50+ years. Third-party tests show modern slabs retain 95% structural integrity after 100,000 cyclic load tests.
Why Choose Specialized Slabs for 2nd Floor Projects
Specialized 2nd floor concrete slab solutions optimize safety and efficiency. With 34% higher shear capacity than generic slabs, they prevent catastrophic failures in high-traffic areas. Partnering with certified suppliers ensures compliance with ASTM C39 and ACI 318 standards, guaranteeing performance across residential and commercial applications.

(slab for 2nd floor)
FAQS on slab for 2nd floor
Q: What materials are best for a slab on the 2nd floor?
A: Reinforced concrete is the most common material for a second-floor slab due to its durability and load-bearing capacity. Lightweight aggregates can reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity. Consult an engineer to ensure compliance with local building codes.
Q: How thick should a 2nd floor concrete slab be?
A: A typical second-floor concrete slab is 4-6 inches thick, depending on load requirements and span. Thicker slabs (6+ inches) may be needed for heavy furniture or equipment. Always follow structural engineering specifications for safety.
Q: What are key design considerations for a slab on the 2nd floor?
A: Prioritize weight distribution to avoid overloading the lower floor. Include proper insulation and vapor barriers to prevent moisture issues. Ensure reinforcement (rebar/mesh) and expansion joints are integrated for stability.
Q: Can a 2nd floor slab be added during a renovation?
A: Yes, but existing structural supports must be evaluated to handle the added weight. Steel beams or additional columns may be required for reinforcement. Professional assessment is critical before installation.
Q: How long does a second-floor concrete slab take to cure?
A: Concrete slabs typically require 7 days to achieve 70% strength and 28 days for full curing. Temperature and humidity affect curing time. Avoid heavy loads until fully cured to prevent cracks.
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
The Durability of Timber Steel FurnitureNewsJul.11,2025
-
How to Assemble Fixed Clamp Scaffolding SafelyNewsJul.11,2025
-
Essential Column Rebar Specifications for High-Rise BuildingsNewsJul.11,2025
-
Common Applications of Steel Keels in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Using Aluminum Scaffolding Ladders Over SteelNewsJul.11,2025
-
Stainless Steel Keel: Analysis of the Triple Advantages of Rigidity, Stability, and LightweightNewsJun.19,2025