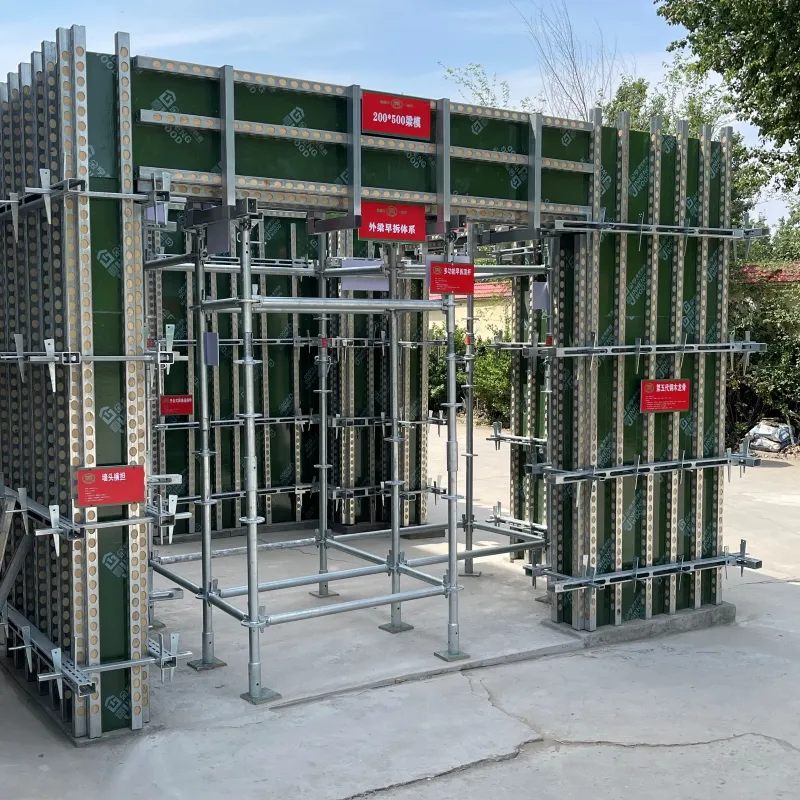
1월 . 20, 2025 15:32
Back to list
Accessories
For those navigating the intricacies of modern construction, the topic of the 2nd floor concrete slab stands as a significant area of interest. Foundational to multi-level buildings, its importance cannot be understated. Drawing on a blend of experience, technical expertise, authority, and trustworthiness, we delve into the nuances that define its use and success in contemporary architecture.
Experience in weather adaptation is another element where our expertise shines. Climates impact the concrete pouring schedules and the curing time. Understanding regional variances and implementing measures such as cold-weather concreting techniques or the application of curing compounds attunes the 2nd floor concrete slab to cope with its environmental challenges. Additionally, advancements in technology have enriched the realm of second floor slabs. The use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) facilitates precise visualization and planning, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency. Simulation software anticipates stress points and can preemptively resolve potential issues, ensuring the slab performs exceptionally well under real-world conditions. As sustainable practices become more crucial, the industry has taken strides in this direction for concrete slabs. Employing eco-friendly practices such as using slag cement or fly ash not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances the slab's longevity by mitigating chemical reactions that cause deterioration. This embodies the construction sector’s dedication to environmentally responsible methods without sacrificing structural integrity or safety. The 2nd floor concrete slab exemplifies the intersection of a deep-seated tradition with avant-garde innovation. Its development from simple support structures into sophisticated components of building design encapsulates the perpetual evolution of construction practices. By relying on lived experience, profound expertise, unwavering authority, and a steadfast commitment to trust, the modern interpretation of this essential element sets a high standard in the architectural and construction communities. For professionals and enthusiasts alike, it stands as a testament to the discipline’s resilience and forward-thinking nature.
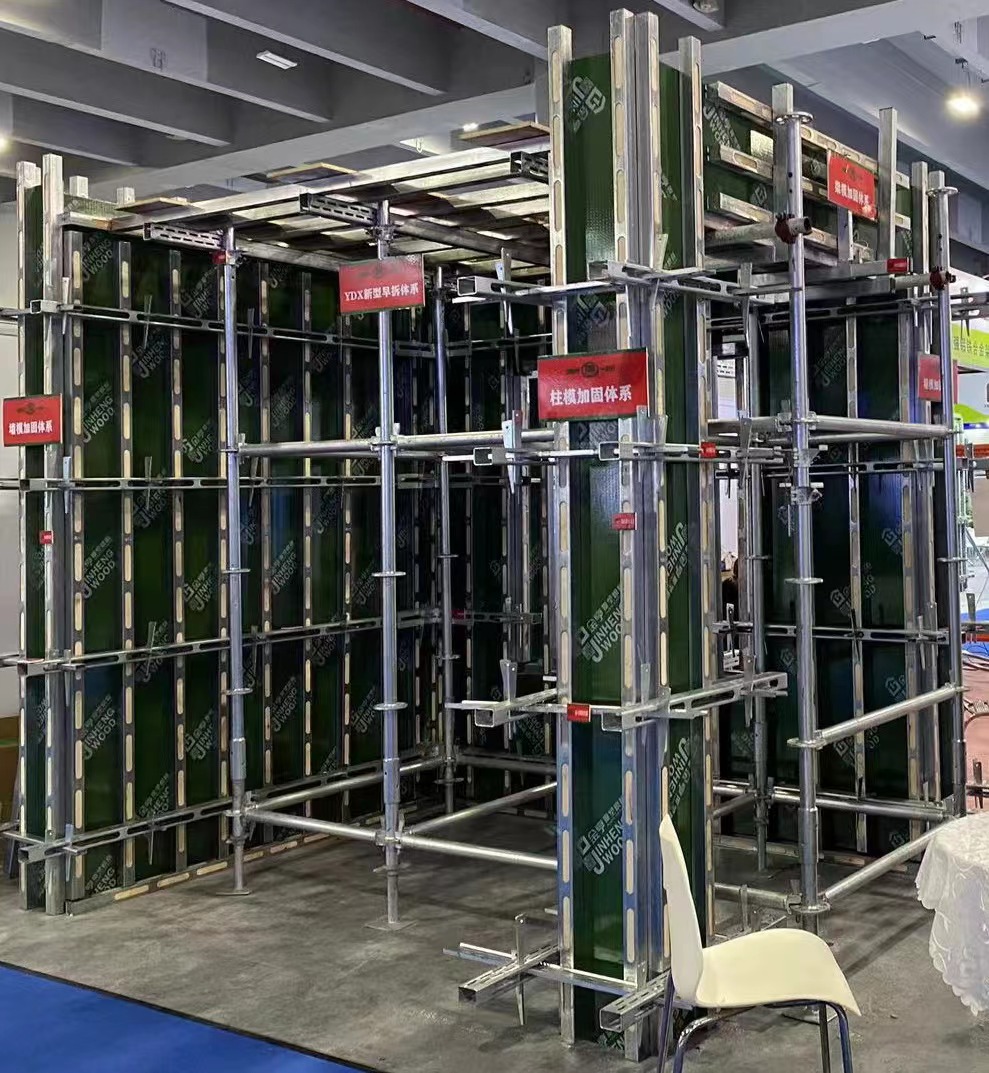


Experience in weather adaptation is another element where our expertise shines. Climates impact the concrete pouring schedules and the curing time. Understanding regional variances and implementing measures such as cold-weather concreting techniques or the application of curing compounds attunes the 2nd floor concrete slab to cope with its environmental challenges. Additionally, advancements in technology have enriched the realm of second floor slabs. The use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) facilitates precise visualization and planning, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency. Simulation software anticipates stress points and can preemptively resolve potential issues, ensuring the slab performs exceptionally well under real-world conditions. As sustainable practices become more crucial, the industry has taken strides in this direction for concrete slabs. Employing eco-friendly practices such as using slag cement or fly ash not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances the slab's longevity by mitigating chemical reactions that cause deterioration. This embodies the construction sector’s dedication to environmentally responsible methods without sacrificing structural integrity or safety. The 2nd floor concrete slab exemplifies the intersection of a deep-seated tradition with avant-garde innovation. Its development from simple support structures into sophisticated components of building design encapsulates the perpetual evolution of construction practices. By relying on lived experience, profound expertise, unwavering authority, and a steadfast commitment to trust, the modern interpretation of this essential element sets a high standard in the architectural and construction communities. For professionals and enthusiasts alike, it stands as a testament to the discipline’s resilience and forward-thinking nature.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
The Durability of Timber Steel FurnitureNewsJul.11,2025
-
How to Assemble Fixed Clamp Scaffolding SafelyNewsJul.11,2025
-
Essential Column Rebar Specifications for High-Rise BuildingsNewsJul.11,2025
-
Common Applications of Steel Keels in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Using Aluminum Scaffolding Ladders Over SteelNewsJul.11,2025
-
Stainless Steel Keel: Analysis of the Triple Advantages of Rigidity, Stability, and LightweightNewsJun.19,2025
Related Products