जनवरी . 16, 2025 00:55
Back to list
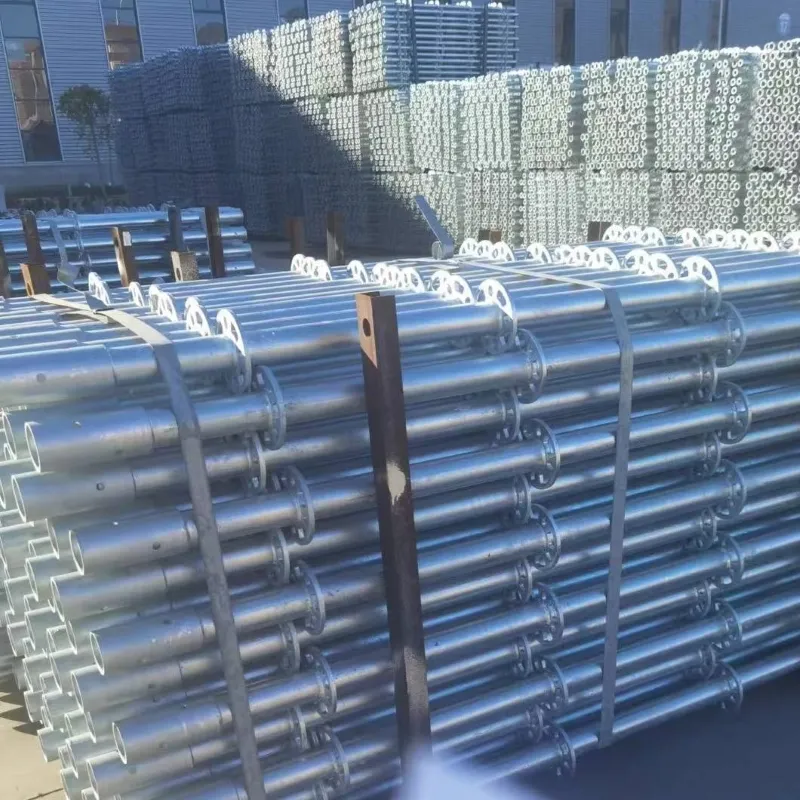
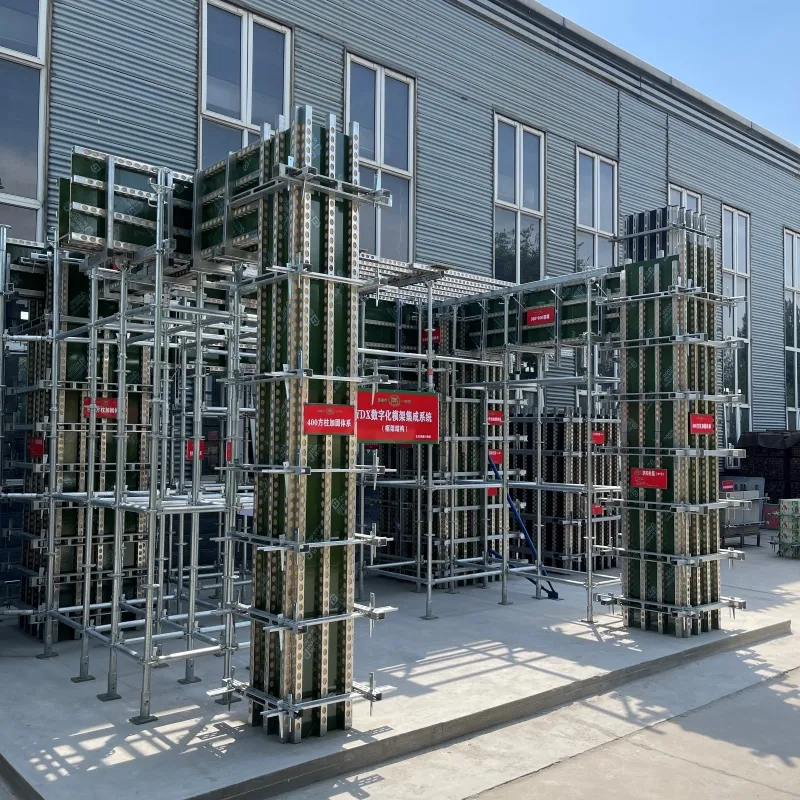
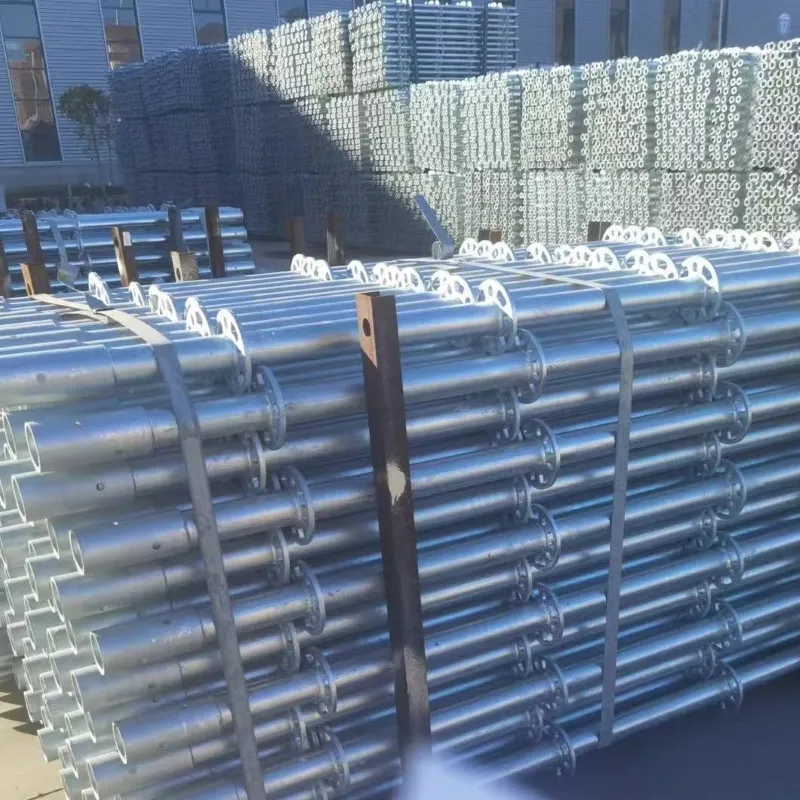
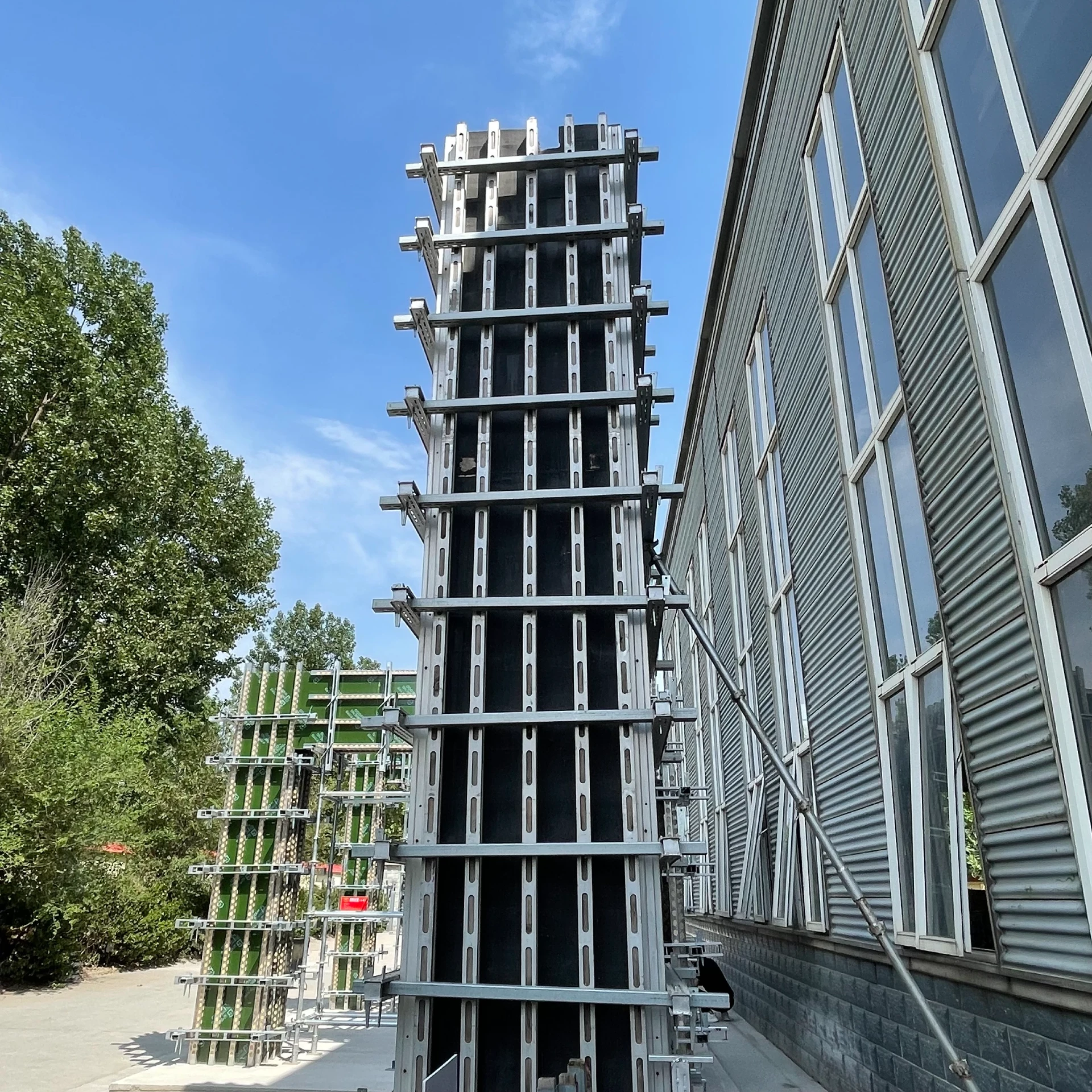
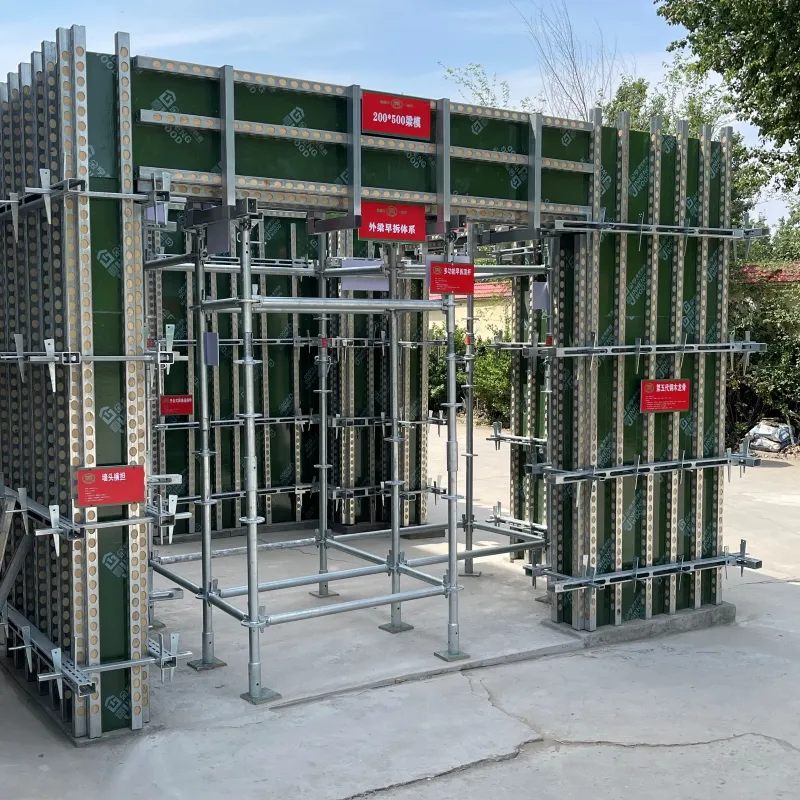
suspended formwork
Suspended formwork represents a crucial innovation in modern construction methods, transforming how engineers and builders approach challenging structural designs. Leveraging the unique benefits this method provides not only enhances structural integrity but also advances construction efficiency significantly.
Furthermore, the economic implications are a decisive factor when considering suspended formwork. Julia Benton, a financial analyst specialized in construction, explains that although initial investments in training and equipment can be substantial, the reduction in labor costs and project timelines can significantly improve overall project profitability. In many cases, the speed of installation and reduced need for extensive ground support lead to a tangible decrease in resource expenditure. In terms of environmental impact, which has become a priority in modern construction projects, suspended formwork offers considerable advantages. The reduced need for ground-based scaffolding minimizes the environmental footprint, as fewer resources are required for assembly and transportation. Environmental engineer Lisa Garvey points out that suspended formwork aligns with green building practices by reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency. Trustworthiness in implementation is bolstered by adherence to international construction standards and regulations, such as the Eurocodes and American Standards. Projects using suspended formwork often undergo rigorous inspections and testing to certify compliance and safety, promoting industry-wide trust in their use. In conclusion, suspended formwork is reshaping the landscape of modern construction. It offers an amalgam of efficiency, innovation, safety, and environmental responsibility, supported by robust expertise and authoritative practice. Engaging with suspended formwork not only ensures state-of-the-art construction solutions but also confirms commitment to progressive building philosophies and sustainability principles. As this method continues to evolve, it stands as a testament to the ingenuity and forward-thinking spirit of the construction industry.
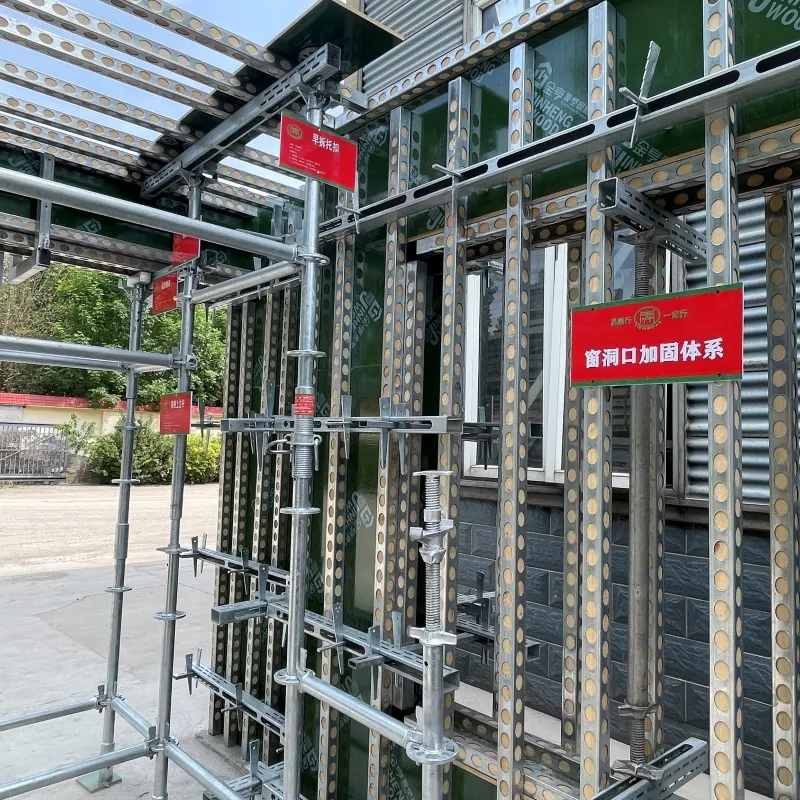


Furthermore, the economic implications are a decisive factor when considering suspended formwork. Julia Benton, a financial analyst specialized in construction, explains that although initial investments in training and equipment can be substantial, the reduction in labor costs and project timelines can significantly improve overall project profitability. In many cases, the speed of installation and reduced need for extensive ground support lead to a tangible decrease in resource expenditure. In terms of environmental impact, which has become a priority in modern construction projects, suspended formwork offers considerable advantages. The reduced need for ground-based scaffolding minimizes the environmental footprint, as fewer resources are required for assembly and transportation. Environmental engineer Lisa Garvey points out that suspended formwork aligns with green building practices by reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency. Trustworthiness in implementation is bolstered by adherence to international construction standards and regulations, such as the Eurocodes and American Standards. Projects using suspended formwork often undergo rigorous inspections and testing to certify compliance and safety, promoting industry-wide trust in their use. In conclusion, suspended formwork is reshaping the landscape of modern construction. It offers an amalgam of efficiency, innovation, safety, and environmental responsibility, supported by robust expertise and authoritative practice. Engaging with suspended formwork not only ensures state-of-the-art construction solutions but also confirms commitment to progressive building philosophies and sustainability principles. As this method continues to evolve, it stands as a testament to the ingenuity and forward-thinking spirit of the construction industry.
Share
Latest news
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
The Durability of Timber Steel FurnitureNewsJul.11,2025
-
How to Assemble Fixed Clamp Scaffolding SafelyNewsJul.11,2025
-
Essential Column Rebar Specifications for High-Rise BuildingsNewsJul.11,2025
-
Common Applications of Steel Keels in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Using Aluminum Scaffolding Ladders Over SteelNewsJul.11,2025
-
Stainless Steel Keel: Analysis of the Triple Advantages of Rigidity, Stability, and LightweightNewsJun.19,2025
Related Products