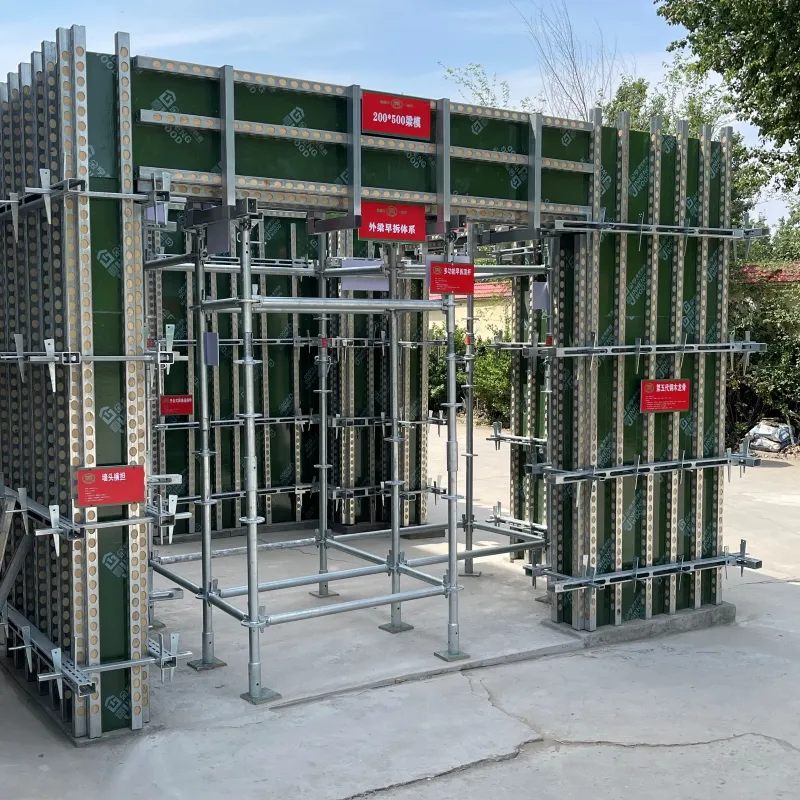
shuttering and scaffolding
Shuttering and Scaffolding Essential Elements in Construction
In the world of construction, the terms “shuttering” and “scaffolding” are often used interchangeably by outsiders, but they refer to distinct yet crucial components in the building process. Both play vital roles in ensuring structural integrity, worker safety, and efficient project execution. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of shuttering and scaffolding, exploring their definitions, uses, variations, and impact on modern construction.
Understanding Shuttering
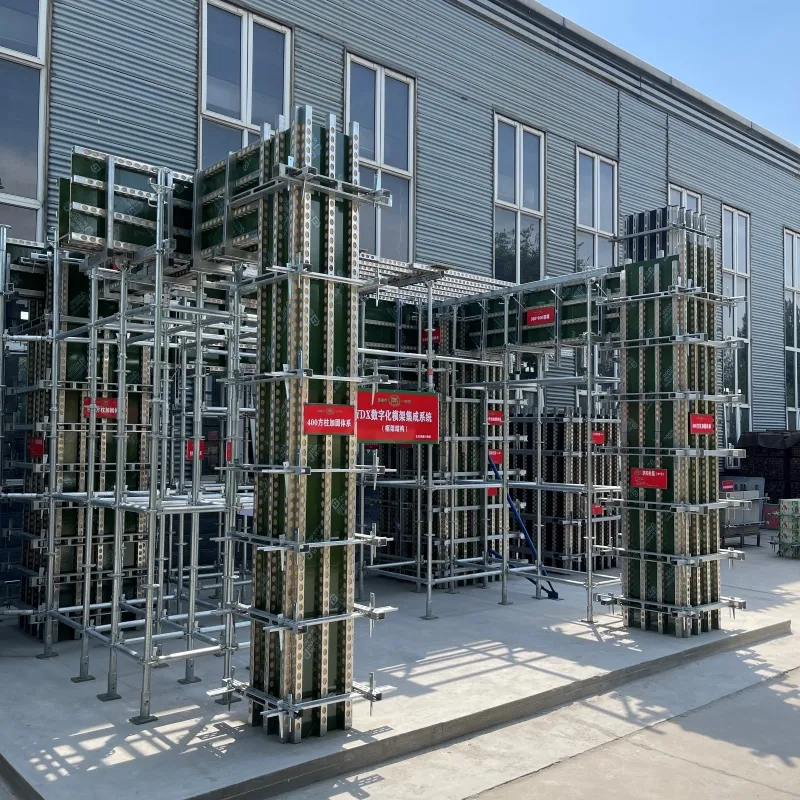
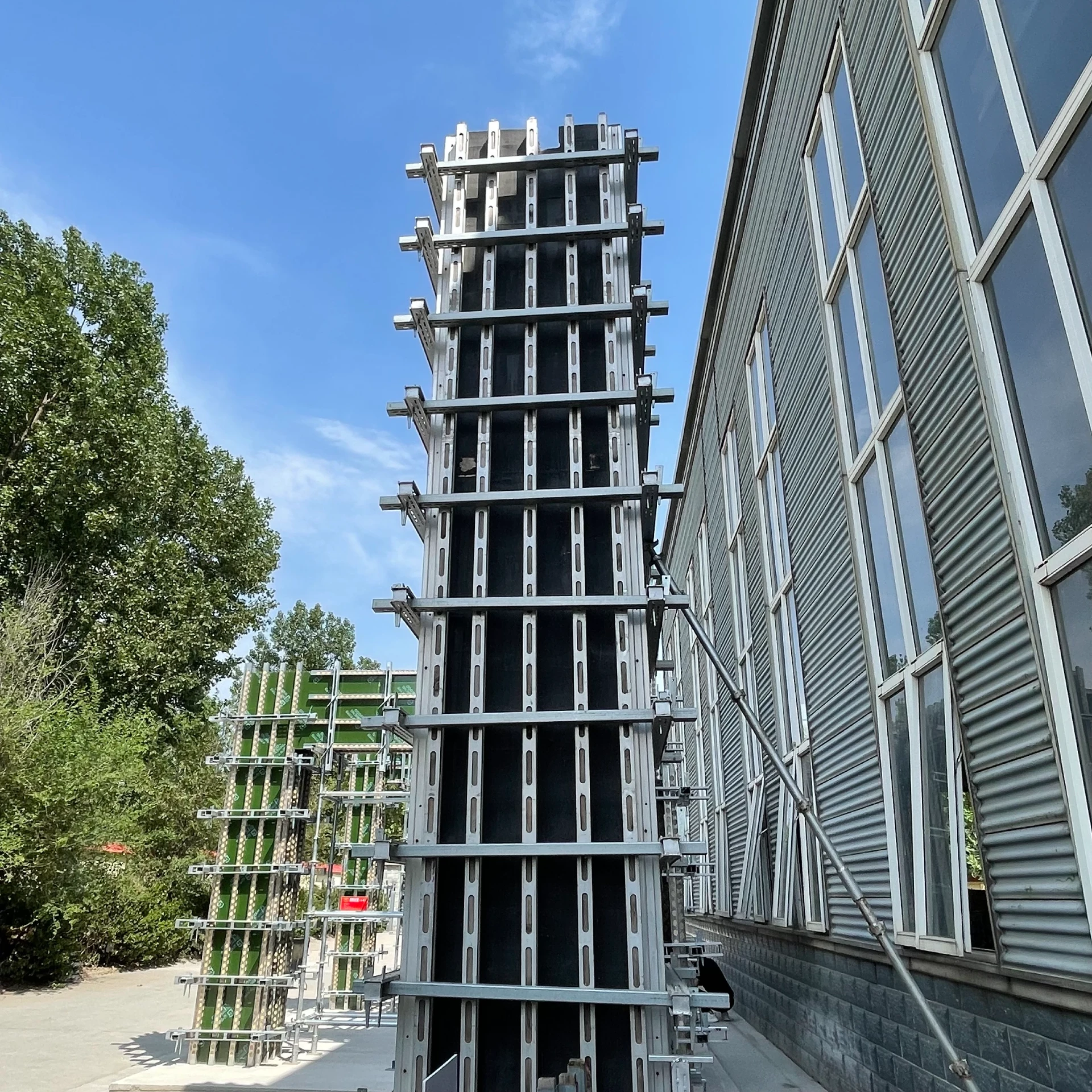
Shuttering, also known as formwork, refers to the temporary structure used to hold concrete in place until it hardens enough to support itself. It is an integral part of the casting process in which concrete is poured into molds to create various structural elements like beams, slabs, and columns. Shuttering can be made from a variety of materials, including plywood, steel, aluminum, and plastic, each chosen for its specific properties and cost-effectiveness.
One of the primary considerations in shuttering is the weight of the concrete it will support. Freshly poured concrete can weigh as much as 150 pounds per cubic foot, requiring robust materials and careful engineering to prevent collapse. Additionally, the design of the shuttering must be precise to ensure that the finished concrete element meets specified dimensions and structural requirements.
Shuttering provides numerous advantages. It enables construction teams to achieve complex shapes and designs, thereby allowing for architectural creativity. High-quality shuttering minimizes surface imperfections and reduces the need for additional finishing work, ultimately saving time and resources. As the demand for rapid construction processes escalates, innovative shuttering solutions, including reusable and modular systems, are becoming increasingly popular.
The Role of Scaffolding
Scaffolding, on the other hand, refers to the temporary structures that provide support and access for workers during construction activities. Unlike shuttering, scaffolding is not meant to be a part of the final product but serves as a platform to facilitate work at various heights and locations. It is essential for ensuring safety when constructing buildings or performing renovations, especially at elevated levels.
shuttering and scaffolding
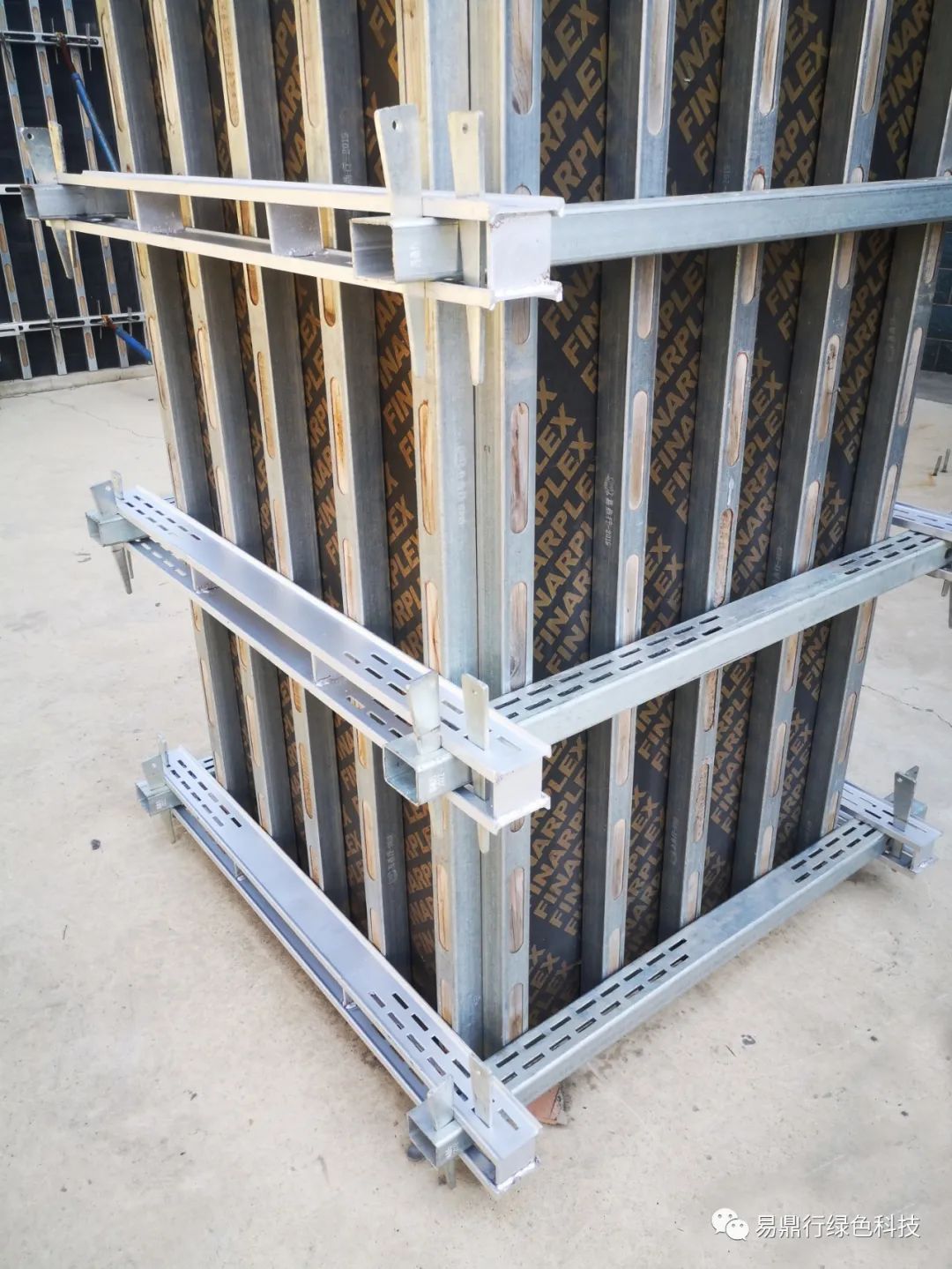

Scaffolding is primarily composed of tubes or pipes, couplers, and boards, which can be assembled to create a stable platform. There are different types of scaffolding systems, including tube and clamp scaffolding, frame scaffolding, and system scaffolding. Each type has its unique advantages and is chosen based on factors such as project size, duration, and site conditions.
The safety of workers is paramount in scaffolding design. Regulations often dictate specific load capacities, access points, and safety features such as guardrails and toe boards to minimize the risk of accidents. As new technologies emerge, advanced scaffolding systems equipped with integrated safety features and innovative designs are being developed to enhance worker protection and project efficiency.
Integration and Innovation
While shuttering and scaffolding serve different purposes, their successful integration is key to the overall efficiency of a construction project. Both require careful planning, skilled labor, and adherence to safety standards. The construction industry is continuously evolving, with new materials and technologies enhancing both shuttering and scaffolding systems.
For example, the emergence of hybrid materials in shuttering is leading to lighter yet stronger forms that are easier to transport and assemble. Similarly, digital scaffolding solutions that incorporate 3D modeling and augmented reality are streamlining the assembly process and improving safety outcomes.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a focal point in construction. Many companies are seeking to minimize waste in both shuttering and scaffolding by investing in reusable systems and eco-friendly materials. The shift towards green building practices is not only beneficial for the environment but also enhances the public perception of the construction industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while shuttering and scaffolding may appear similar, they serve distinct purposes that are integral to the construction process. Understanding their roles ensures the successful execution of projects while maintaining high safety and quality standards. As technology advances and the industry evolves, the importance of adapting innovative solutions for shuttering and scaffolding will only grow, paving the way for safer, more efficient, and sustainable construction practices in the future.
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
The Durability of Timber Steel FurnitureNewsJul.11,2025
-
How to Assemble Fixed Clamp Scaffolding SafelyNewsJul.11,2025
-
Essential Column Rebar Specifications for High-Rise BuildingsNewsJul.11,2025
-
Common Applications of Steel Keels in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Using Aluminum Scaffolding Ladders Over SteelNewsJul.11,2025
-
Stainless Steel Keel: Analysis of the Triple Advantages of Rigidity, Stability, and LightweightNewsJun.19,2025