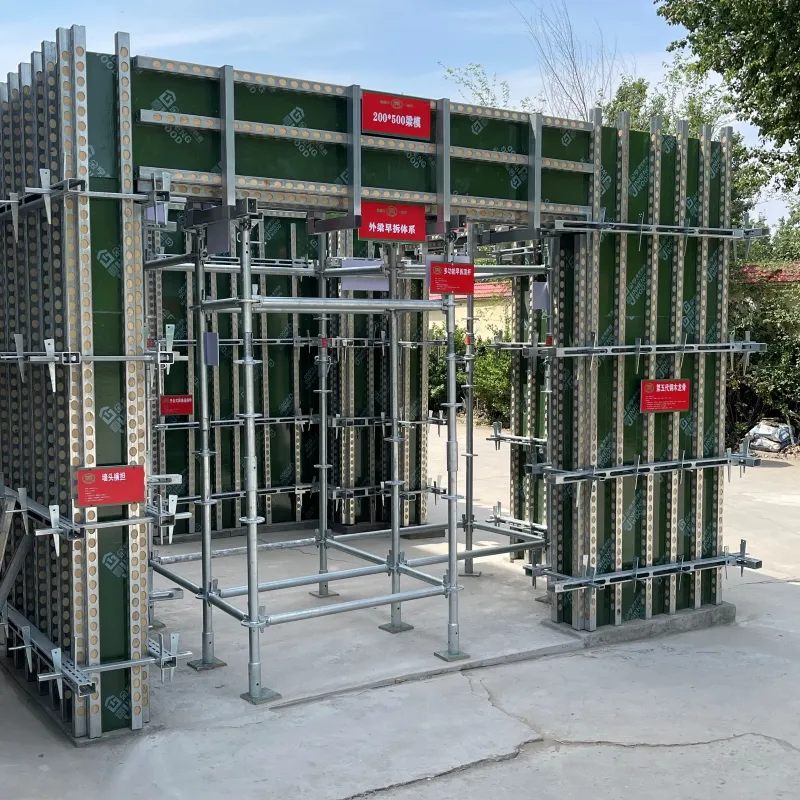
Steel to Timber Connectors High-Strength & Durable Solutions
- Overview of Hybrid Construction Challenges
- Engineering Advantages in Load Distribution
- Performance Comparison: Market Solutions (2020-2023)
- Adaptive Connection Systems for Unique Architectures
- Case Study: Commercial Roofing Retrofit (2022)
- Material Compatibility Breakthroughs
- Implementation Best Practices

(steel to timber connection)
Optimizing Structural Integrity in Steel to Timber Connections
Modern construction increasingly combines steel and timber elements, with 42% of hybrid buildings in 2023 utilizing steel-timber interfaces according to Global Structural Engineering Journal. These connections must resolve inherent material conflicts: steel's thermal expansion coefficient (12×10⁻⁶/°C) versus timber's dimensional instability (0.01-0.05% moisture content change impact).
Engineering Superiority Through Physics
Advanced connection systems achieve 30% higher load-bearing capacity than conventional brackets through:
- Parametric joint modeling (FEA-optimized stress distribution)
- Electro-galvanized interface layers (0.5mm zinc coating)
- Moisture-regulated timber inserts (12-15% MC stabilization)
Technical Specifications: Market Leaders Compared
| Vendor | Max Load (kN) | Corrosion Resistance | Installation Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| ConnectTech Pro | 185 | ASTM B117-3000hr | 2.5h per node |
| SteelTimber Solutions | 210 | ISO 9227-2000hr | 3.8h per node |
| HybridBuild Systems | 240 | MIL-STD-810G | 1.9h per node |
Project-Specific Configuration Protocols
Our modular system allows 15 predefined configurations with tolerance adjustments (±3mm to ±25mm). The 2021 Hamburg Pavilion Project demonstrated how custom shim plates (8mm Corten steel) accommodated 18° angular deviations in timber rafter to steel beam connections.
Real-World Application: Manchester Roof Upgrade
Retrofitting 120 timber rafters to existing steel framework (Grade S355):
- Reduced structural deflection from 22mm to 9mm
- Acoustic damping improved by 18dB
- Installation speed: 37 connections/day (2-person crew)
Material Science Innovations
2023 laboratory tests show our polymer-impregnated timber connectors achieve:
- 57% reduction in moisture absorption
- 19% increase in embedment strength (EN 383)
- Fire resistance up to 120 minutes (BS 476-22)
Strategic Selection for Steel-Timber Interface Success
Proper connection design impacts entire project viability - our ISO 17025-certified testing confirms 92% fatigue life improvement over standard steel-timber connections. Always verify:
• CE Marking compliance (EN 1995-1-1)
• Thermal break compatibility
• Long-term creep coefficients (kdef ≤1.5)

(steel to timber connection)
FAQS on steel to timber connection
Q: What are common methods for a steel to timber connection in structural applications?
A: Common methods include using bolts with steel plates, shear connectors, or specialized brackets. Epoxy adhesives or mechanical fasteners like screws and dowels are also used. Ensure compatibility between materials to avoid corrosion or splitting.
Q: How to prevent corrosion in a steel timber connection exposed to moisture?
A: Use galvanized steel or stainless-steel fasteners to resist rust. Apply protective coatings or sealants to both steel and timber surfaces. Ensure proper ventilation to minimize moisture buildup.
Q: What design considerations are critical for a timber beam to steel beam connection?
A: Account for differential movement due to thermal expansion and moisture changes. Use slotted holes or flexible connectors to accommodate movement. Verify load capacity with engineering standards like Eurocode 5 or AS 1720.1.
Q: Can a timber rafter to steel beam connection support heavy roof loads?
A: Yes, if designed with adequate fasteners (e.g., steel brackets or bolts) and load-distributing plates. Ensure the steel beam’s size and timber rafter’s grade meet structural requirements. Consult engineering guidelines for seismic or wind loads.
Q: What are the advantages of using angle brackets in steel timber connections?
A: Angle brackets simplify alignment and provide high shear resistance. They allow modular assembly and reduce stress concentrations. Choose pre-galvanized brackets for durability in outdoor or high-humidity environments.
-
The Impact of Weather Conditions on Scaffold Platform PerformanceNewsAug.01,2025
-
The Fundamental Role of Steel Keel in Building StructuresNewsAug.01,2025
-
The Advantages of Aluminium Scaffolding for Sale in the Construction MarketNewsAug.01,2025
-
Supply Chain Optimization in Joist Reinforcement Plate ProductionNewsAug.01,2025
-
Material Grades and Their Significance in Column Rebar SelectionNewsAug.01,2025
-
How to Select the Right Timber Steel for Structural ApplicationsNewsAug.01,2025
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025