Fév . 14, 2025 10:42
Back to list
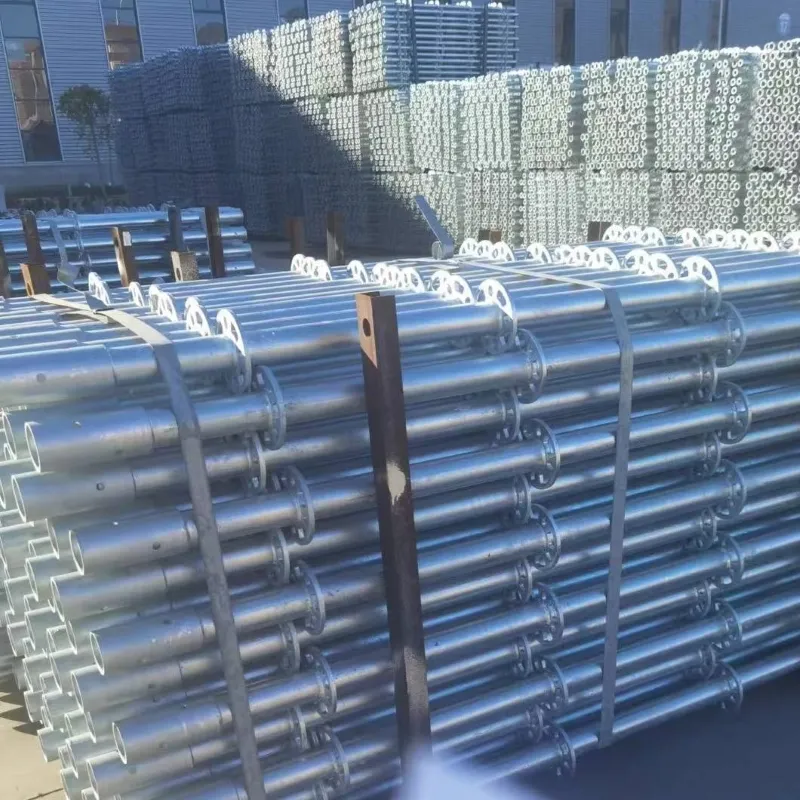
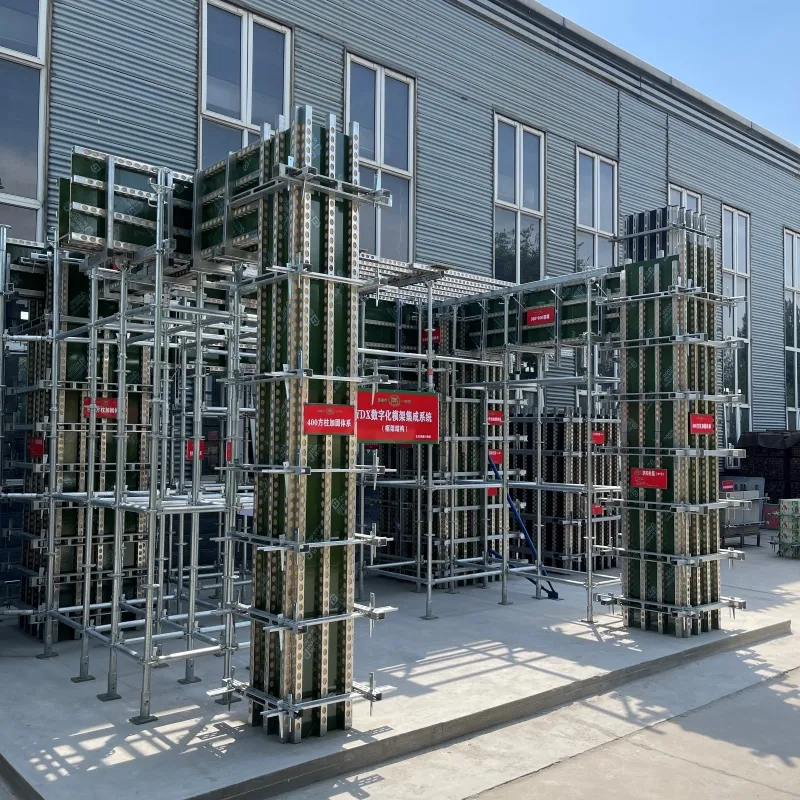
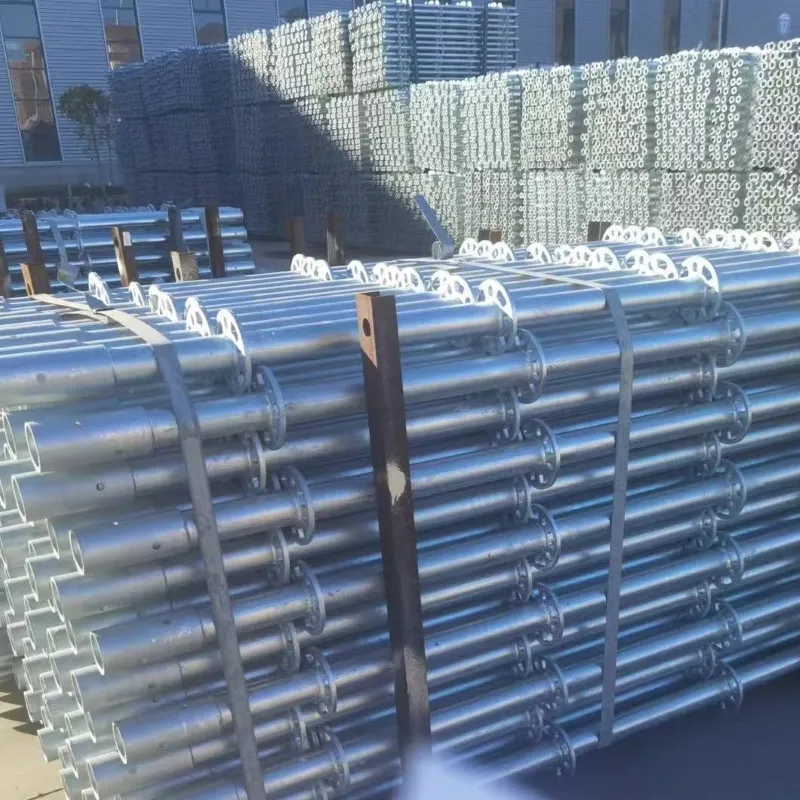
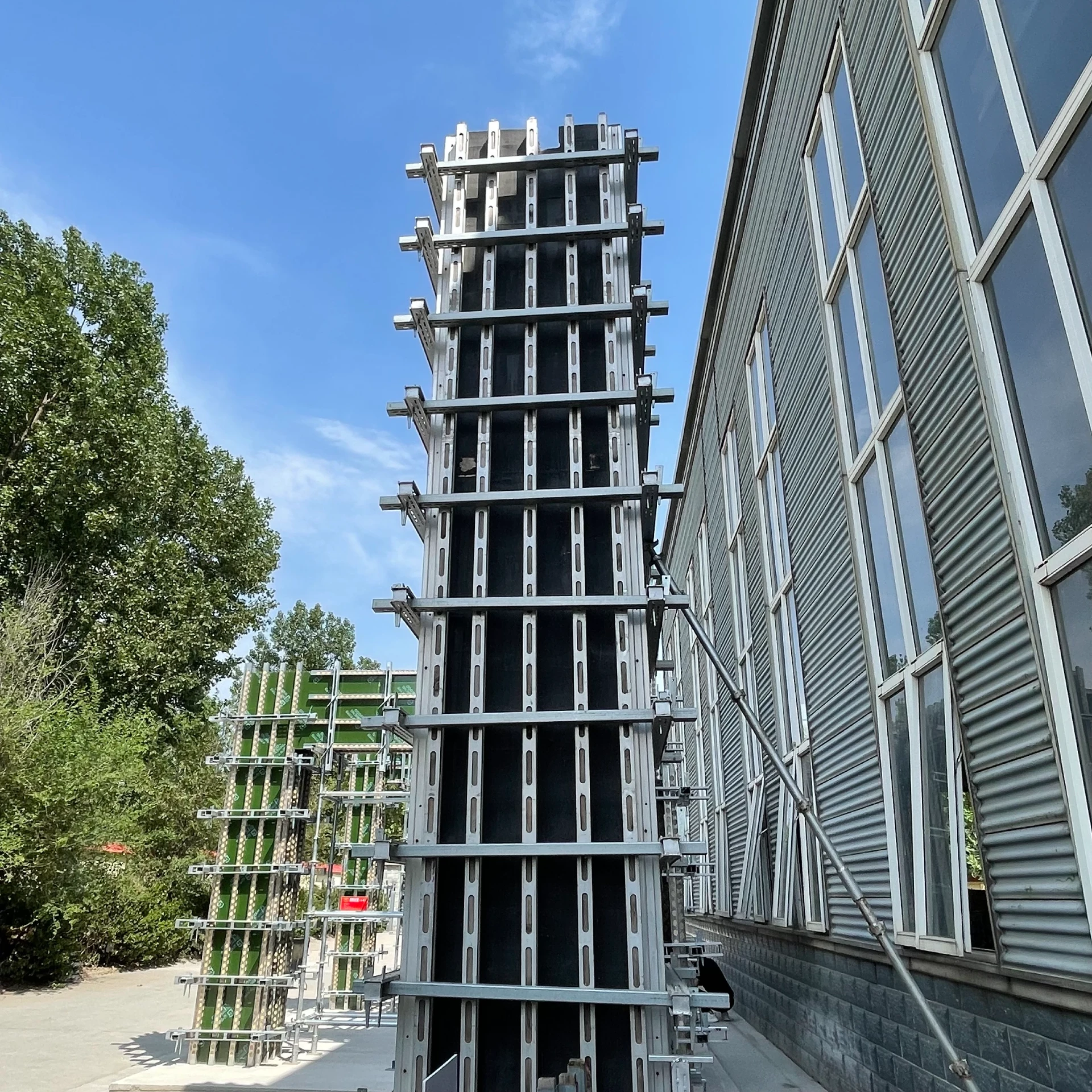
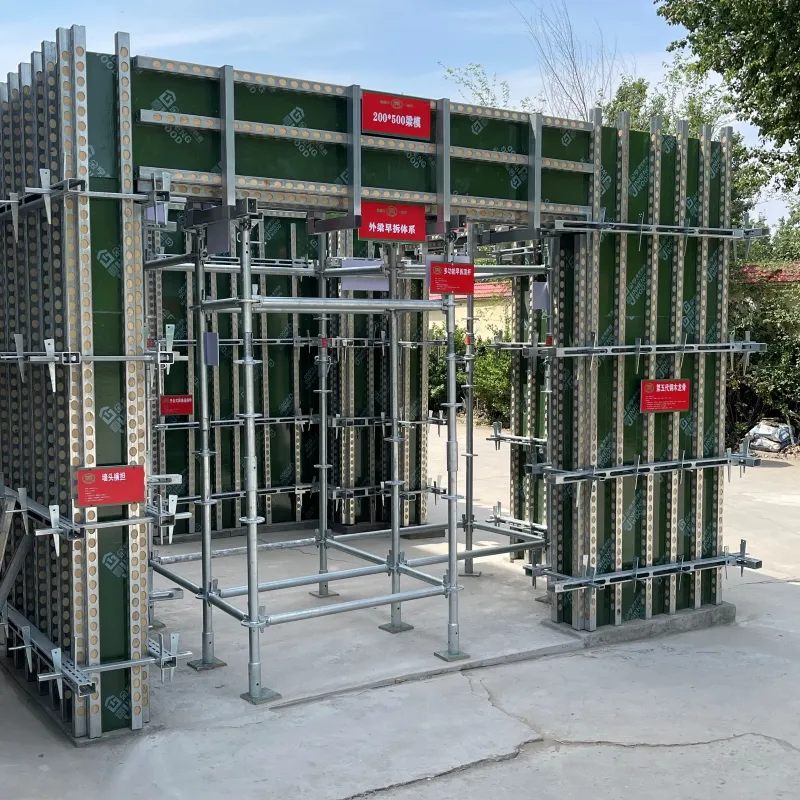
shoring scaffold
Shoring scaffolds play a critical role in ensuring both safety and efficiency in construction projects across diverse industries. As a fundamental component in structural support, they possess a multitude of applications ranging from simple residential buildings to large-scale commercial enterprises. Understanding the nuances of shoring scaffolds, both from a practical and theoretical standpoint, can significantly impact the success of construction endeavors.
Authoritativeness in the realm of shoring scaffolds is established through adherence to industry standards and regulations. Organizations such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) provide comprehensive guidelines to ensure both the structural integrity of the scaffold and the safety of the workers. Following these codes not only legalizes the construction process but also promotes a culture of safety and reliability, which is paramount for long-term sustainability in construction practices. Trustworthiness in deploying shoring scaffolds is achieved through rigorous inspection and maintenance procedures. Regular checks must be conducted to detect any signs of wear and tear, corrosion, or misalignment that could compromise safety. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule ensures that scaffolds remain in optimal condition, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents and project delays. Moreover, having trained professionals on-site who are knowledgeable about the setup, operation, and dismantling of these structures further enhances their reliability, building confidence among all stakeholders involved in the project. In conclusion, the strategic implementation of shoring scaffolds is a testament to their undeniable value in the construction sector. By leveraging practical experience, specialized knowledge, adherence to regulatory standards, and rigorous maintenance practices, stakeholders can optimize their use effectively and safely. Understanding these vital elements will not only enhance project efficiency but also contribute to setting new benchmarks in construction safety and excellence. This multifaceted approach ensures that shoring scaffolds will continue to be a cornerstone in modern construction, fostering innovation and growth within the industry.
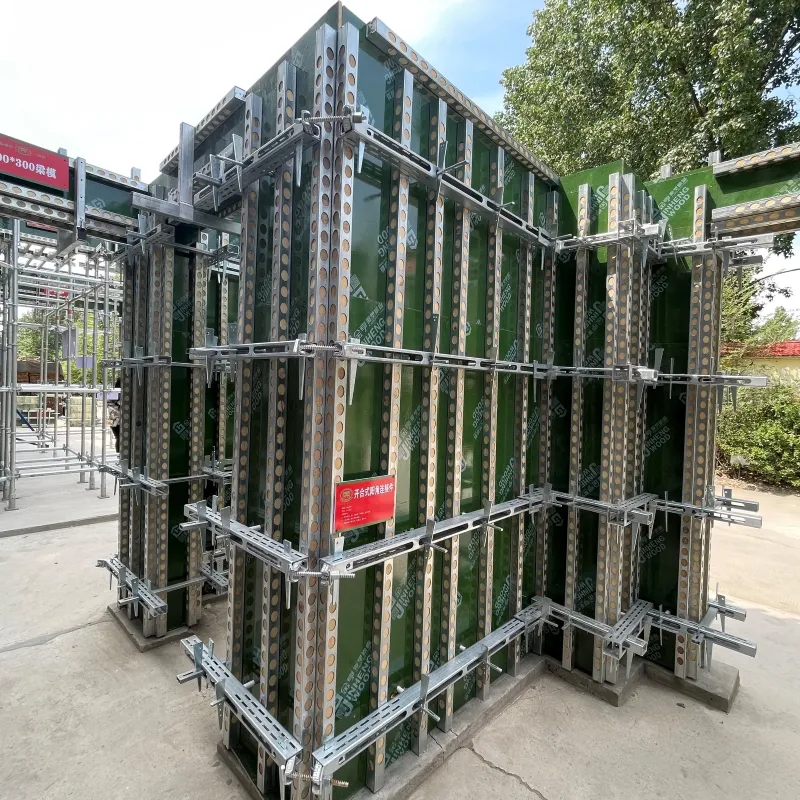


Authoritativeness in the realm of shoring scaffolds is established through adherence to industry standards and regulations. Organizations such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) provide comprehensive guidelines to ensure both the structural integrity of the scaffold and the safety of the workers. Following these codes not only legalizes the construction process but also promotes a culture of safety and reliability, which is paramount for long-term sustainability in construction practices. Trustworthiness in deploying shoring scaffolds is achieved through rigorous inspection and maintenance procedures. Regular checks must be conducted to detect any signs of wear and tear, corrosion, or misalignment that could compromise safety. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule ensures that scaffolds remain in optimal condition, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents and project delays. Moreover, having trained professionals on-site who are knowledgeable about the setup, operation, and dismantling of these structures further enhances their reliability, building confidence among all stakeholders involved in the project. In conclusion, the strategic implementation of shoring scaffolds is a testament to their undeniable value in the construction sector. By leveraging practical experience, specialized knowledge, adherence to regulatory standards, and rigorous maintenance practices, stakeholders can optimize their use effectively and safely. Understanding these vital elements will not only enhance project efficiency but also contribute to setting new benchmarks in construction safety and excellence. This multifaceted approach ensures that shoring scaffolds will continue to be a cornerstone in modern construction, fostering innovation and growth within the industry.
Share
Latest news
-
The Importance of Reinforcement Bar in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
The Durability of Timber Steel FurnitureNewsJul.11,2025
-
How to Assemble Fixed Clamp Scaffolding SafelyNewsJul.11,2025
-
Essential Column Rebar Specifications for High-Rise BuildingsNewsJul.11,2025
-
Common Applications of Steel Keels in ConstructionNewsJul.11,2025
-
Benefits of Using Aluminum Scaffolding Ladders Over SteelNewsJul.11,2025
-
Stainless Steel Keel: Analysis of the Triple Advantages of Rigidity, Stability, and LightweightNewsJun.19,2025
Related Products