يناير . 24, 2025 03:09
Back to list
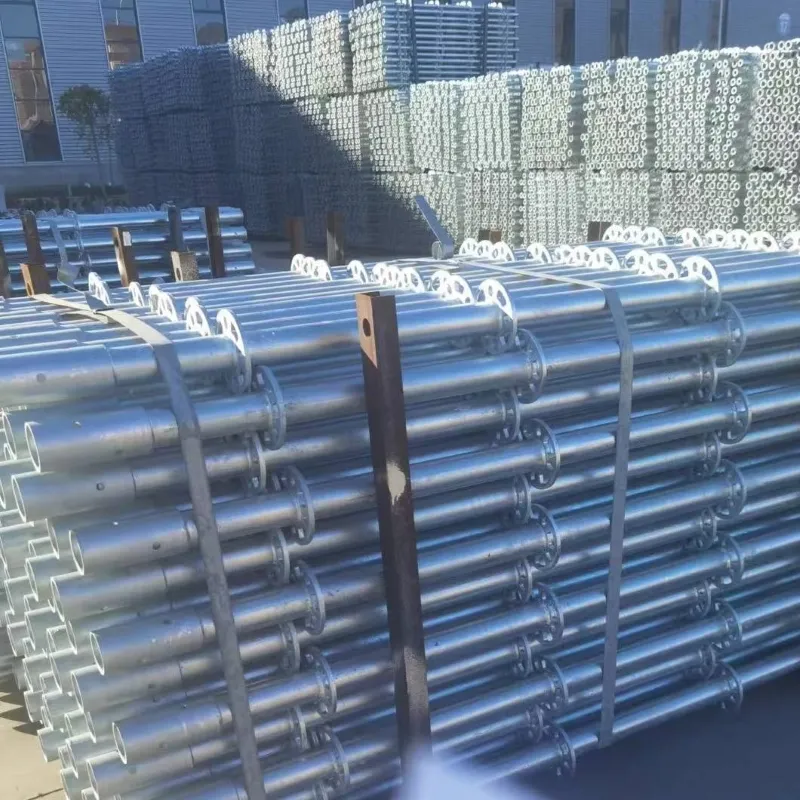
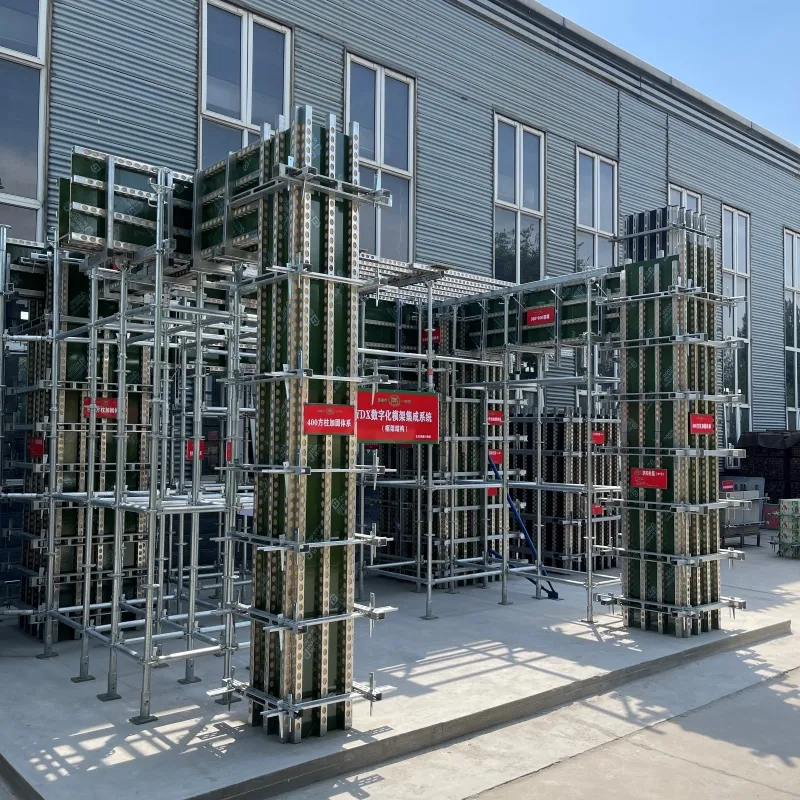
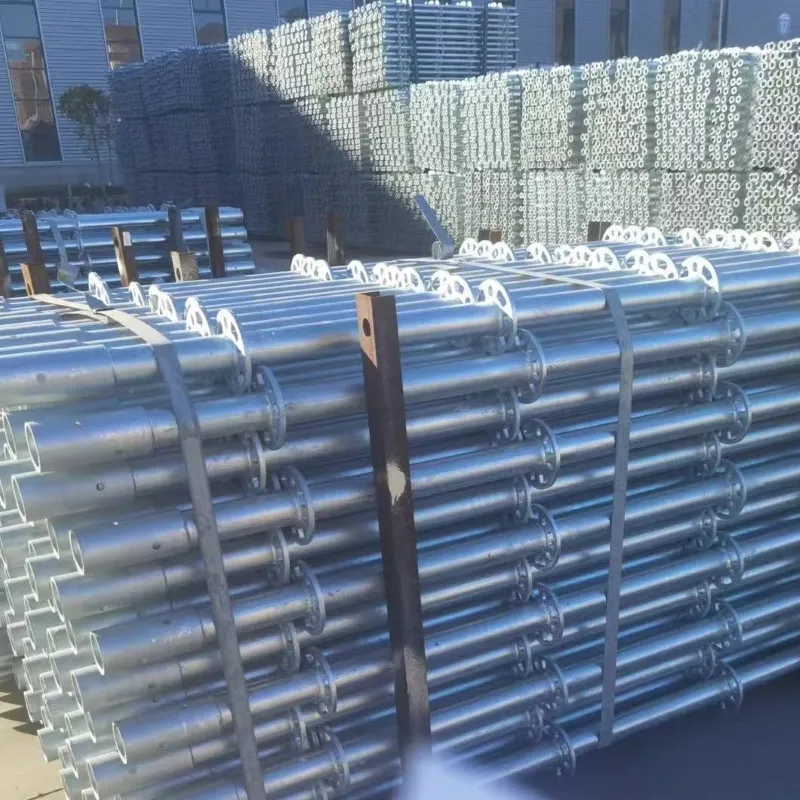
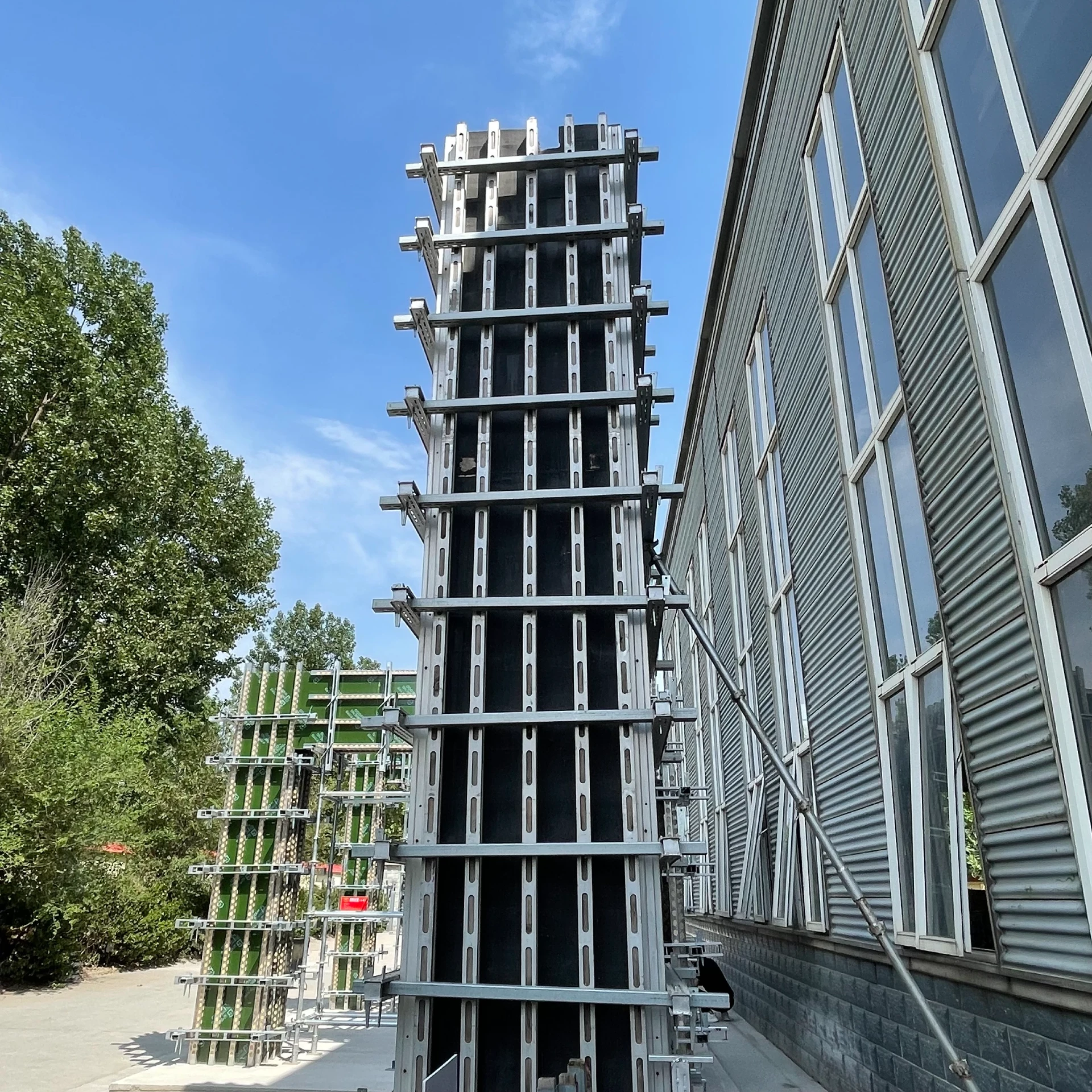
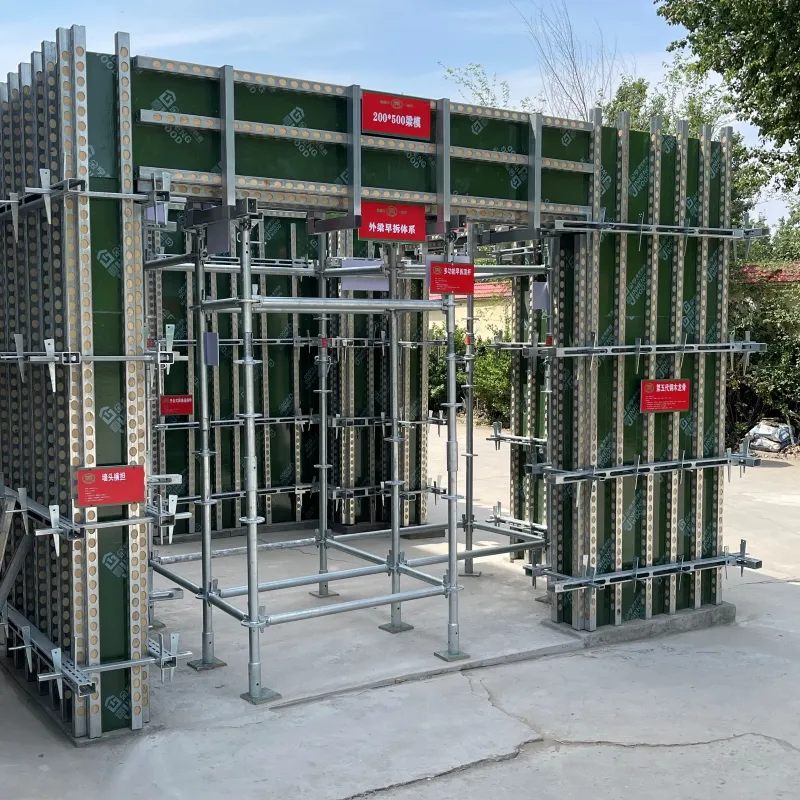
scaffolding
Suspended ground floor slabs represent a critical innovation in modern construction, offering an advanced solution for various building challenges. By delicately balancing between specialized engineering methods and practical construction requirements, suspended slabs provide an elevated flooring solution, mainly used in areas where traditional ground slabs may suffer due to soil instability or slope issues.
Experience plays a fundamental role in managing the intricacies associated with suspended ground floor slabs. Contractors with a profound understanding of construction dynamics and strong project management practices ensure the slab is constructed efficiently and to the highest standards. This proficiency minimizes risks associated with project delays, cost overruns, or structural failures, building a foundation of trust with stakeholders through reliable service delivery and adherence to the engineering blueprints. From an authoritative perspective, suspended ground floor slabs are acknowledged by international structural regulation bodies and standards organizations. Many experts and industry publications frequently highlight case studies where suspended slabs have significantly contributed to successful projects, especially in terrains where traditional foundation approaches would fail. This recognition attests to the robustness and reliability of suspended slabs as a high-caliber choice in complex construction scenarios. Institutional trust is underpinned by empirical evidence showing that suspended ground floor slabs have not only served residential buildings but also performed exceptionally in retail and industrial projects. Regular inspections, using both visual methods and advanced technologies such as ground penetrating radar (GPR), further ensure the integrity and durability of these installations over time. In conclusion, suspended ground floor slabs offer significant advantages in settings that demand innovative construction strategies. They embody an ideal union of expertise and practical experience, augmented by industry authority and trustworthiness, which collectively guarantee a robust, safe, and cost-effective solution for modern architectural challenges. Their implementation reflects a commitment to technical excellence and a proactive approach to managing diverse environmental conditions.
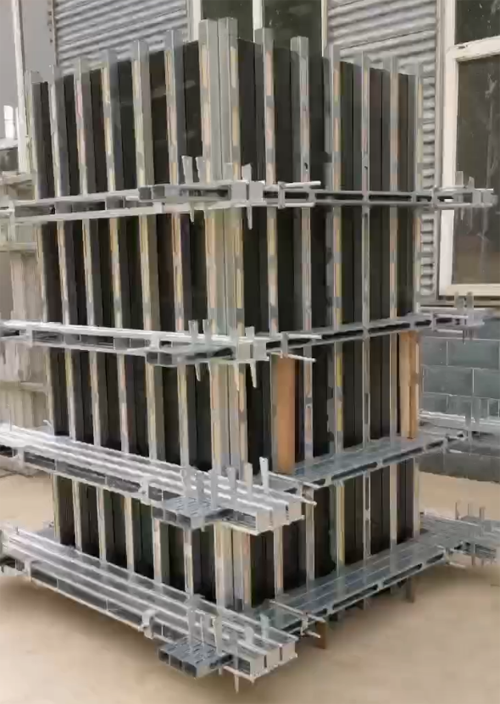
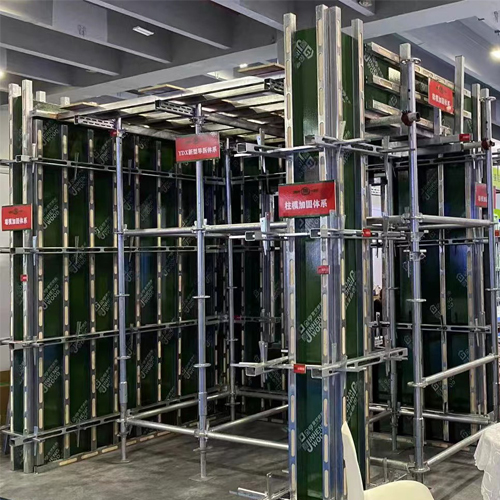


Experience plays a fundamental role in managing the intricacies associated with suspended ground floor slabs. Contractors with a profound understanding of construction dynamics and strong project management practices ensure the slab is constructed efficiently and to the highest standards. This proficiency minimizes risks associated with project delays, cost overruns, or structural failures, building a foundation of trust with stakeholders through reliable service delivery and adherence to the engineering blueprints. From an authoritative perspective, suspended ground floor slabs are acknowledged by international structural regulation bodies and standards organizations. Many experts and industry publications frequently highlight case studies where suspended slabs have significantly contributed to successful projects, especially in terrains where traditional foundation approaches would fail. This recognition attests to the robustness and reliability of suspended slabs as a high-caliber choice in complex construction scenarios. Institutional trust is underpinned by empirical evidence showing that suspended ground floor slabs have not only served residential buildings but also performed exceptionally in retail and industrial projects. Regular inspections, using both visual methods and advanced technologies such as ground penetrating radar (GPR), further ensure the integrity and durability of these installations over time. In conclusion, suspended ground floor slabs offer significant advantages in settings that demand innovative construction strategies. They embody an ideal union of expertise and practical experience, augmented by industry authority and trustworthiness, which collectively guarantee a robust, safe, and cost-effective solution for modern architectural challenges. Their implementation reflects a commitment to technical excellence and a proactive approach to managing diverse environmental conditions.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
Top Scaffolding Solutions for Every Construction ProjectNewsApr.21,2025
-
Scaffolding Solutions for Every ProjectNewsApr.21,2025
-
Innovative Construction Solutions for a Stronger FutureNewsApr.21,2025
-
Essential Steel Keel Solutions for Maximum Protection and PerformanceNewsApr.21,2025
-
Building a solid foundation: The importance of high-quality concrete reinforcement accessoriesNewsApr.21,2025
-
Effective Reinforcement for Stronger StructuresNewsApr.21,2025
-
The Essential Role of Timber and Steel in Modern ConstructionNewsMar.10,2025
Related Products